Node.js 操作 MySQL 数据库
MySQL 是一个开源的关系型 SQL 数据库,这也是目前使用量最多的数据库之一,仅次于 Oracle。MySQL 开源免费,资源占用少,从大型企业网站到个人博客网站,MySQL 都能满足需求。
之前写了 Node.js 操作 SQLite 数据库 ,这里就继续来写常用的另一个数据库 MySQL。
使用 npm 安装 mysql 模块:
npm install mysql --save连接数据库
下面连接到一个本地的 blog 数据库:
const mysql = require('mysql');
// 创建数据库连接
const db = mysql.createConnection({
host: 'localhost',
user: 'root',
password: '123456',
database: 'blog'
});
// 连接到数据库
db.connect(err => {
// 出错就输出异常
if (err) throw err;
console.log('成功连接');
});
// 关闭数据库连接
db.end();使用 mysql 的 createConnection 可以创建一个数据库连接,createConnection 需要接收一个数据库信息的对象,下面是对象参数说明:
host:数据库服务器地址user:数据库用户名password:数据库密码database:要打开的数据库名称port:端口,默认为 3306connectTimeout:超时,以毫秒为单位,默认为 10000
使用 createConnection 创建连接后可以调用 connect 连接到数据库,connect 也可以传入一个回调函数,回调函数的参数就是错误信息。
在使用完毕后可以调用 end 方法来关闭数据库连接。
增加、删除、修改数据
在我连接的 blog 数据库中有一张名为 user 的数据表,表结构如下:
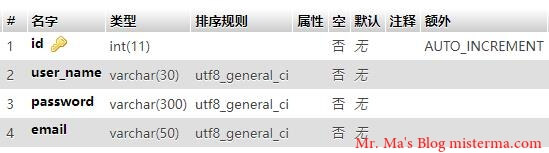
下面的操作都会使用这张表。
我这里写的是 Node.js 操作 MySQL,主要是 Node.js,不会详细的写 MySQL 的 SQL 语句,关于 MySQL 的简单使用可以看我博客 数据库 分类的文章。
插入数据
下面在 user 中插入一条数据:
// SQL 语句
const sql = `
INSERT INTO user
(user_name, password, email)
VALUES
('Mr. Ma', '123', 'i@misterma.com')
`;
// 执行 SQL 查询
db.query(sql, (err, result) => {
if (err) throw err;
// 输出受影响的行数
console.log(result.affectedRows);
});上面 user 表中的 id 是自动增加的,在插入的时候,我只插入了 user_name 、password 、email 。
在写 SQL 的时候,字符串、日期时间、枚举类型需要使用引号包裹,数字和浮点数类型不需要引号包裹。
使用 query 可以执行一个 SQL 查询,第一个参数是 SQL,第二个参数是执行完成的回调函数。执行完成的回调函数可以接收两个参数,第一个是错误信息,第二个是查询结果。
通过查询结果的 affectedRows 可以获取受影响的行数。
删除数据
上面插入数据的时候,插入的内容都是直接写死在 SQL 中的,现实中基本都是动态传入,需要在 SQL 中拼接查询。
下面使用拼接 SQL 的方式删除 user 表中插入的数据:
// 用于传入 SQL 查询的 id 和 email
const id = 2;
const email = 'i@misterma.com';
// SQL 语句
const sql = `
DELETE FROM user
WHERE
id = ${id} AND email = ${mysql.escape(email)}
`;
// 执行 SQL 查询
db.query(sql, (err, result) => {
if (err) throw err;
// 输出受影响的行数
console.log(result.affectedRows);
});在动态传入查询字符串的时候,为了避免特殊符号错误和 SQL 注入,可以先使用 mysql.escape 方法进行转译,传入要转译的字符串,返回转译后的字符串。在拼接 SQL 的时候,使用 mysql.escape 转译过的字符串可以不需要单独的引号包裹。
注意,调用 mysql.escape 转译的时候,需要直接调用 mysql 模块,不是调用 mysql.createConnection 创建连接时返回的数据库对象!
修改数据
mysql 模块和 sqlite3 模块一样,SQL 语句也支持使用 ? 占位符来动态传入内容替换,在使用 ? 占位符时,query 的第二个参数就是替换值,需要传入一个数组,第三个参数就是执行完成的回调函数。
下面修改 user 表的数据,使用 ? 占位符动态传入修改:
// SQL 语句
const sql = `
UPDATE user
SET
user_name = ?, email = ?
WHERE id = ?
`;
// 执行 SQL 查询
db.query(sql, ['changbin1997', 'admin@misterma.com', 1], (err, result) => {
if (err) throw err;
// 输出受影响的行数
console.log(result.affectedRows);
});上面把 user_name 改为 changbin1997 ,email 改为 admin@misterma.com ,修改的是 id 为 1 的条目。
替换占位符的时候,数组元素的数量和位置都是和占位符对应的。
获取自动递增的 ID
大多数数据表应该都有一个自动递增的 id,在插入数据的时候,如果想获取自动递增的 id 也是可以的。
下面再插入一条数据,获取自动递增的 id:
// SQL 语句
const sql = `
INSERT INTO user
(user_name, password, email)
VALUES
('changbin1997', '666', 'mail@misterma.com')
`;
// 执行 SQL 查询
db.query(sql, (err, result) => {
if (err) throw err;
// 输出受影响的行数
console.log(result.affectedRows);
// 输出自动递增的 id
console.log(result.insertId);
});在查询完成的回调函数中,使用查询结果的 insertId 可以获取自动递增的 id,这个 insertId 只能获取一个 id,如果你在一条 SQL 中插入多条数据的话,是无法获取递增 id 的。
下面是完整的查询结果对象:
{
fieldCount: 0,
affectedRows: 1,
insertId: 4,
serverStatus: 2,
warningCount: 0,
message: '',
protocol41: true,
changedRows: 0
}查询数据
下面查询出 user 表的所有内容
// SQL 语句
const sql = `SELECT * FROM user`;
// 执行 SQL 查询
db.query(sql, (err, result) => {
if (err) throw err;
// 输出查询结果
console.log(result);
});查询结果是一个包含对象的数组,如下:
[
{
id: 1,
user_name: 'Mr. Ma',
password: '123456',
email: 'i@misterma.com'
},
{
id: 3,
user_name: 'changbin1997',
password: '666',
email: 'mail@misterma.com'
}
]查询完成的回调函数还可以接收第三个参数,第三个参数是字段信息,下面查询 user 表,输出字段信息:
// SQL 语句
const sql = `SELECT * FROM user`;
// 执行 SQL 查询
db.query(sql, (err, result, fields) => {
if (err) throw err;
// 输出字段信息
console.log(fields);
});我的 user 数据表有 id 、user_name 、password ,email 四个字段,字段信息如下:
[
{
catalog: 'def',
db: 'blog',
table: 'user',
orgTable: 'user',
name: 'id',
orgName: 'id',
charsetNr: 63,
length: 11,
type: 3,
flags: 16899,
decimals: 0,
default: undefined,
zeroFill: false,
protocol41: true
},
{
catalog: 'def',
db: 'blog',
table: 'user',
orgTable: 'user',
name: 'user_name',
orgName: 'user_name',
charsetNr: 33,
length: 90,
type: 253,
flags: 4097,
decimals: 0,
default: undefined,
zeroFill: false,
protocol41: true
},
{
catalog: 'def',
db: 'blog',
table: 'user',
orgTable: 'user',
name: 'password',
orgName: 'password',
charsetNr: 33,
length: 900,
type: 253,
flags: 4097,
decimals: 0,
default: undefined,
zeroFill: false,
protocol41: true
},
{
catalog: 'def',
db: 'blog',
table: 'user',
orgTable: 'user',
name: 'email',
orgName: 'email',
charsetNr: 33,
length: 150,
type: 253,
flags: 4097,
decimals: 0,
default: undefined,
zeroFill: false,
protocol41: true
}
]一次执行多条 SQL
在创建数据库连接的时候,把 multipleStatements 设置为 true 可以开启一次执行多条 SQL 的查询:
const mysql = require('mysql');
// 创建数据库连接
const db = mysql.createConnection({
host: 'localhost',
user: 'root',
password: '123456',
database: 'blog',
multipleStatements: true
});
// 连接到数据库
db.connect(err => {
// 出错就输出异常
if (err) throw err;
console.log('成功连接');
});
const email = 'i@misterma.com';
// SQL 语句
const sql = `
SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = 1;
SELECT COUNT(*) AS count FROM user;
SELECT MD5('www.misterma.com') AS url_md5
`;
// 执行 SQL 查询
db.query(sql, (err, result, fields) => {
if (err) throw err;
// 输出查询结果
console.log(result);
});
// 关闭数据库连接
db.end();上面的第一条 SQL 是查询出 user 表的数据,第二条 SQL 是查询 user 表的总行数,第三条 SQL 是把一个字符串进行 md5 加密,每一条 SQL 之间用分号 ; 分隔,查询结果如下:
[
[
{
id: 1,
user_name: 'changbin1997',
password: '123456',
email: 'admin@misterma.com'
}
],
[
{
count: 2
}
],
[
{
url_md5: '7691d9418a8bee661f889a771753142b'
}
]
]在一次执行多条 SQL 出错的时候,错误信息对象会包含一个 index 属性,这个 index 就是出错的 SQL 的序号,计数从 0 开始。查询的时候,如果有一条 SQL 出错,后面的 SQL 也不会再执行。
版权声明:本文为原创文章,版权归 Mr. Ma's Blog 所有,转载请联系博主获得授权。
本文地址:https://www.misterma.com/archives/931/
如果对本文有什么问题或疑问都可以在评论区留言,我看到后会尽量解答。